# 数据结构:哈希表(散列) Hash
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
原文:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/j78MXMx6D_nDC_bCFvZ05g (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
哈希表的历史
哈希散列的想法在不同的地方独立出现。1953 年 1 月,汉斯·彼得·卢恩 ( Hans Peter Luhn ) 编写了一份IBM内部备忘录,其中使用了散列和链接。开放寻址后来由 AD Linh 在 Luhn 的论文上提出。大约在同一时间,IBM Research的Gene Amdahl、Elaine M. McGraw、Nathaniel Rochester和Arthur Samuel为IBM 701汇编器实现了散列。 线性探测的开放寻址归功于 Amdahl,尽管Ershov独立地有相同的想法。“开放寻址”一词是由W. Wesley Peterson在他的文章中创造的,该文章讨论了大文件中的搜索问题。
# 二、哈希数据结构
哈希表的存在是为了解决能通过O(1)时间复杂度直接索引到指定元素。
这是什么意思呢?通过我们使用数组存放元素,都是按照顺序存放的,当需要获取某个元素的时候,则需要对数组进行遍历,获取到指定的值。如图所示;
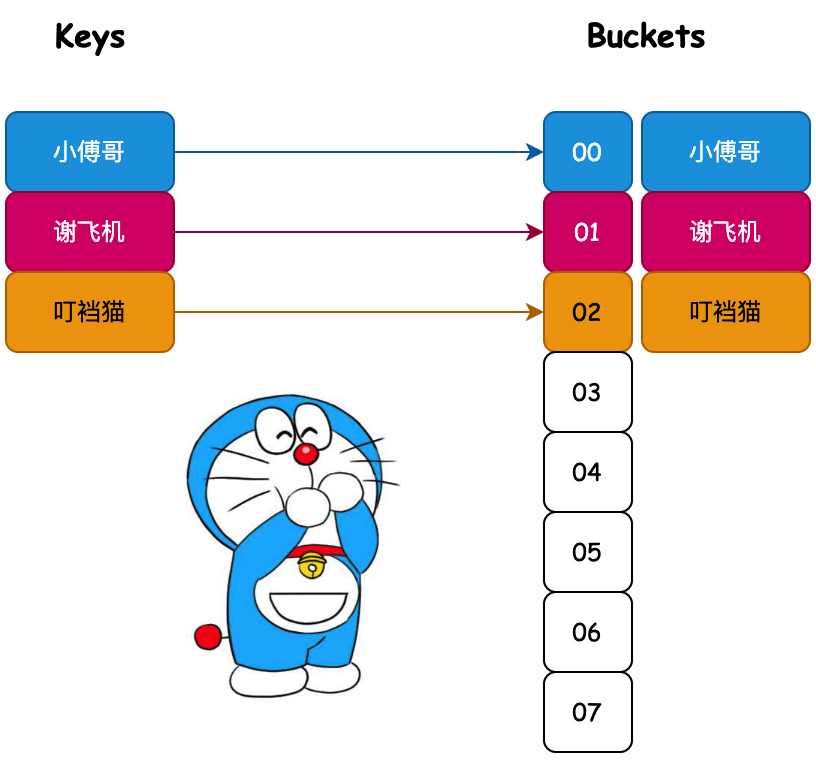
而这样通过循环遍历比对获取指定元素的操作,时间复杂度是O(n),也就是说如果你的业务逻辑实现中存在这样的代码是非常拉胯的。那怎么办呢?这就引入了哈希散列表的设计。
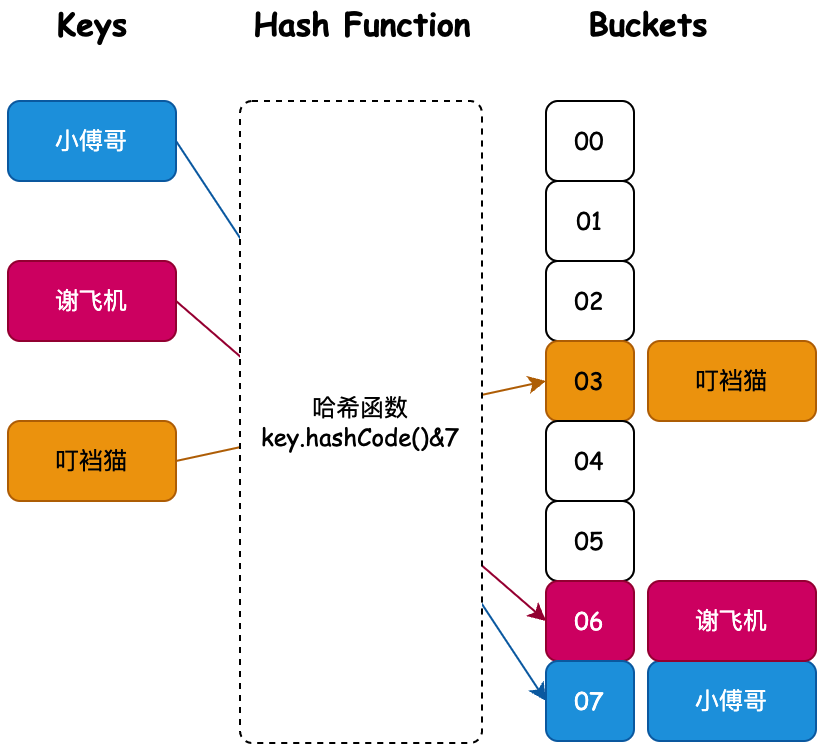
在计算机科学中,一个哈希表(hash table、hash map)是一种实现关联数组的抽象数据结构,该结构将键通过哈希计算映射到值。
也就是说我们通过对一个 Key 值计算它的哈希并与长度为2的n次幂的数组减一做与运算,计算出槽位对应的索引,将数据存放到索引下。那么这样就解决了当获取指定数据时,只需要根据存放时计算索引ID的方式再计算一次,就可以把槽位上对应的数据获取处理,以此达到时间复杂度为O(1)的情况。如图所示;
哈希散列虽然解决了获取元素的时间复杂度问题,但大多数时候这只是理想情况。因为随着元素的增多,很可能发生哈希冲突,或者哈希值波动不大导致索引计算相同,也就是一个索引位置出现多个元素情况。如图所示;
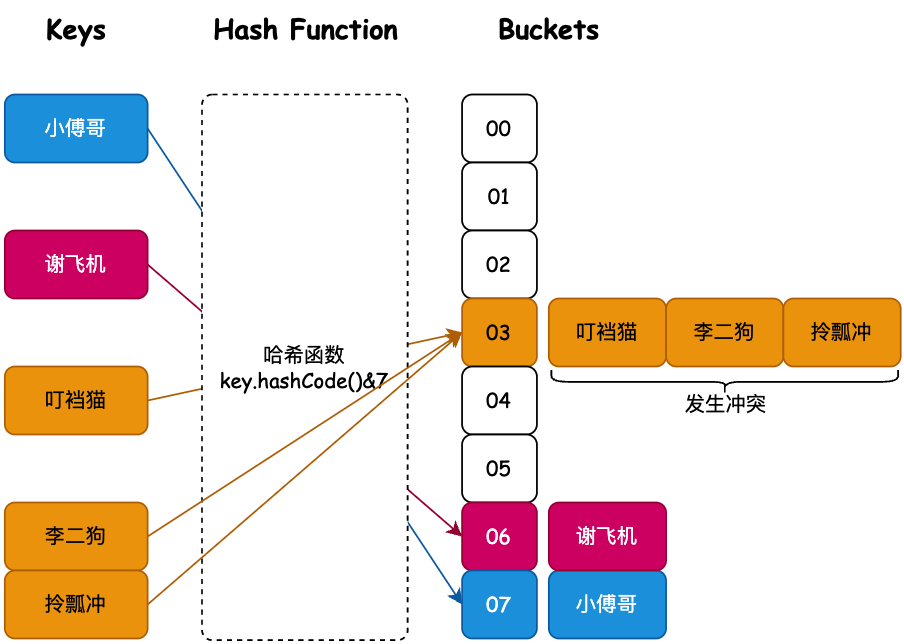
当李二狗、拎瓢冲都有槽位的下标索引03的 叮裆猫 发生冲突时,情况就变得糟糕了,因为这样就不能满足O(1)时间复杂度获取元素的诉求了。
那么此时就出现了一系列解决方案,包括;HashMap 中的拉链寻址 + 红黑树、扰动函数、负载因子、ThreadLocal 的开放寻址、合并散列、杜鹃散列、跳房子哈希、罗宾汉哈希等各类数据结构设计。让元素在发生哈希冲突时,也可以存放到新的槽位,并尽可能保证索引的时间复杂度小于O(n)
# 三、实现哈希散列
哈希散列是一个非常常见的数据结构,无论是我们使用的 HashMap、ThreaLocal 还是你在刷题中位了提升索引效率,都会用到哈希散列。
只要哈希桶的长度由负载因子控制的合理,每次查找元素的平均时间复杂度与桶中存储的元素数量无关。另外许多哈希表设计还允许对键值对的任意插入和删除,每次操作的摊销固定平均成本。
好,那么介绍了这么多,小傅哥带着大家做几个关于哈希散列的数据结构,通过实践来了解会更加容易搞懂。
- 源码地址:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)-
Java 算法与数据结构 - 本章源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms/tree/main/data-structures/src/main/java/hash_table (opens new window)
- 扩展资料:《Java 面经手册》 (opens new window) - 本章涉及到的拉链寻址、开放寻址在 Java API 中的 HashMap、ThreadLocal 有完整实现,同时涉及了扰动函数、负载因子、斐波那契散列,可以扩展学习。
# 1. 哈希碰撞
说明:通过模拟简单 HashMap 实现,去掉拉链寻址等设计,验证元素哈希索引位置碰撞。
public class HashMap01<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final Object[] tab = new Object[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
tab[idx] = value;
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
return (V) tab[idx];
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
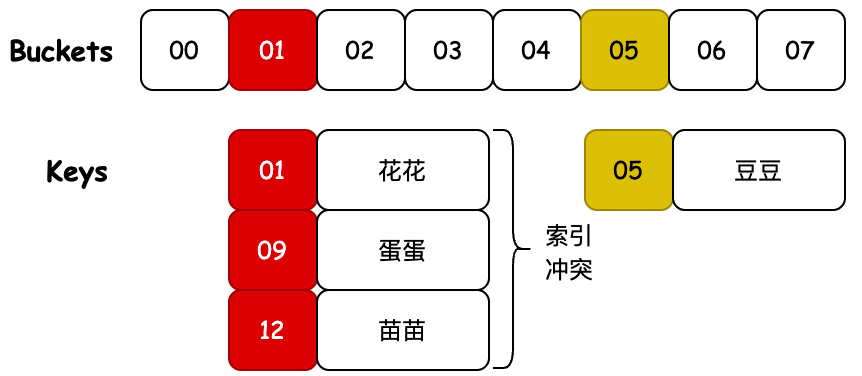
- HashMap01 的实现只是通过哈希计算出的下标,散列存放到固定的数组内。那么这样当发生元素下标碰撞时,原有的元素就会被新的元素替换掉。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap01() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap01<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("02", "豆豆");
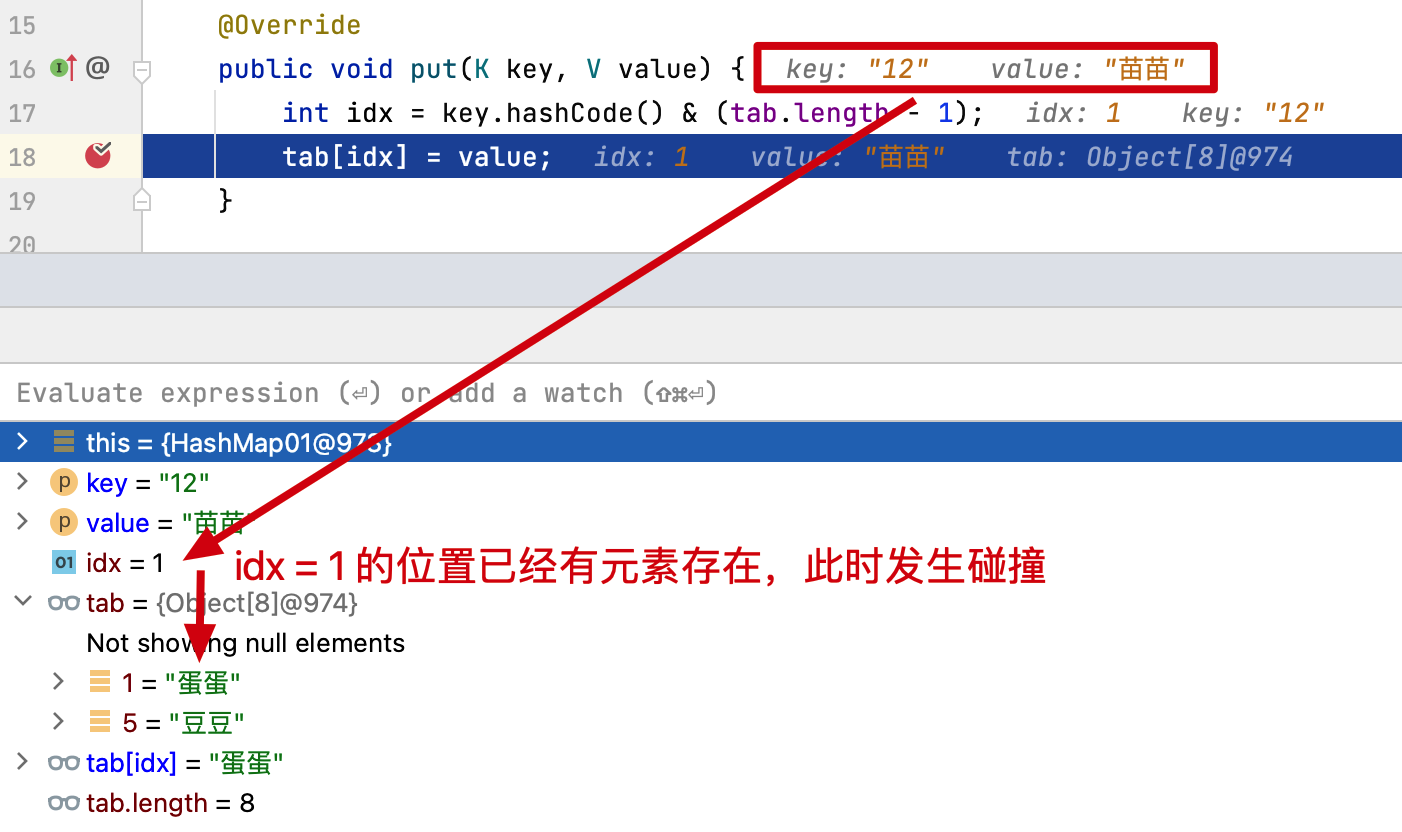
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
06:58:41.691 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
06:58:41.696 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:苗苗
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
- 通过测试结果可以看到,碰撞前 map.get("01") 的值是
花花,两次下标索引碰撞后存放的值则是苗苗 - 这也就是使用哈希散列必须解决的一个问题,无论是在已知元素数量的情况下,通过扩容数组长度解决,还是把碰撞的元素通过链表存放,都是可以的。
# 2. 拉链寻址
说明:既然我们没法控制元素不碰撞,但我们可以对碰撞后的元素进行管理。比如像 HashMap 中拉链法一样,把碰撞的元素存放到链表上。这里我们就来简化实现一下。
public class HashMap02BySeparateChaining<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final LinkedList<Node<K, V>>[] tab = new LinkedList[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
if (tab[idx] == null) {
tab[idx] = new LinkedList<>();
tab[idx].add(new Node<>(key, value));
} else {
tab[idx].add(new Node<>(key, value));
}
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
for (Node<K, V> kvNode : tab[idx]) {
if (key.equals(kvNode.getKey())) {
return kvNode.value;
}
}
return null;
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
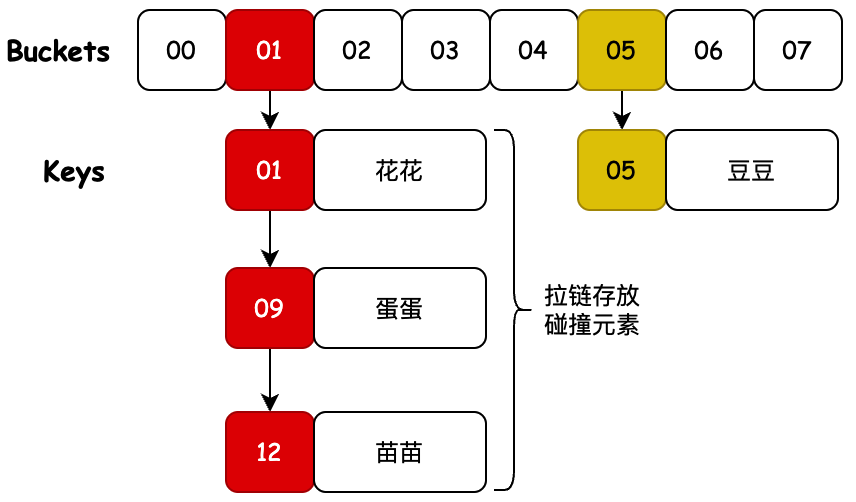
- 因为元素在存放到哈希桶上时,可能发生下标索引膨胀,所以这里我们把每一个元素都设定成一个 Node 节点,这些节点通过 LinkedList 链表关联,当然你也可以通过 Node 节点构建出链表 next 元素即可。
- 那么这时候在发生元素碰撞,相同位置的元素就都被存放到链表上了,获取的时候需要对存放多个元素的链表进行遍历获取。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap02() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap02BySeparateChaining<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("05", "豆豆");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
07:21:16.654 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:22:44.651 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
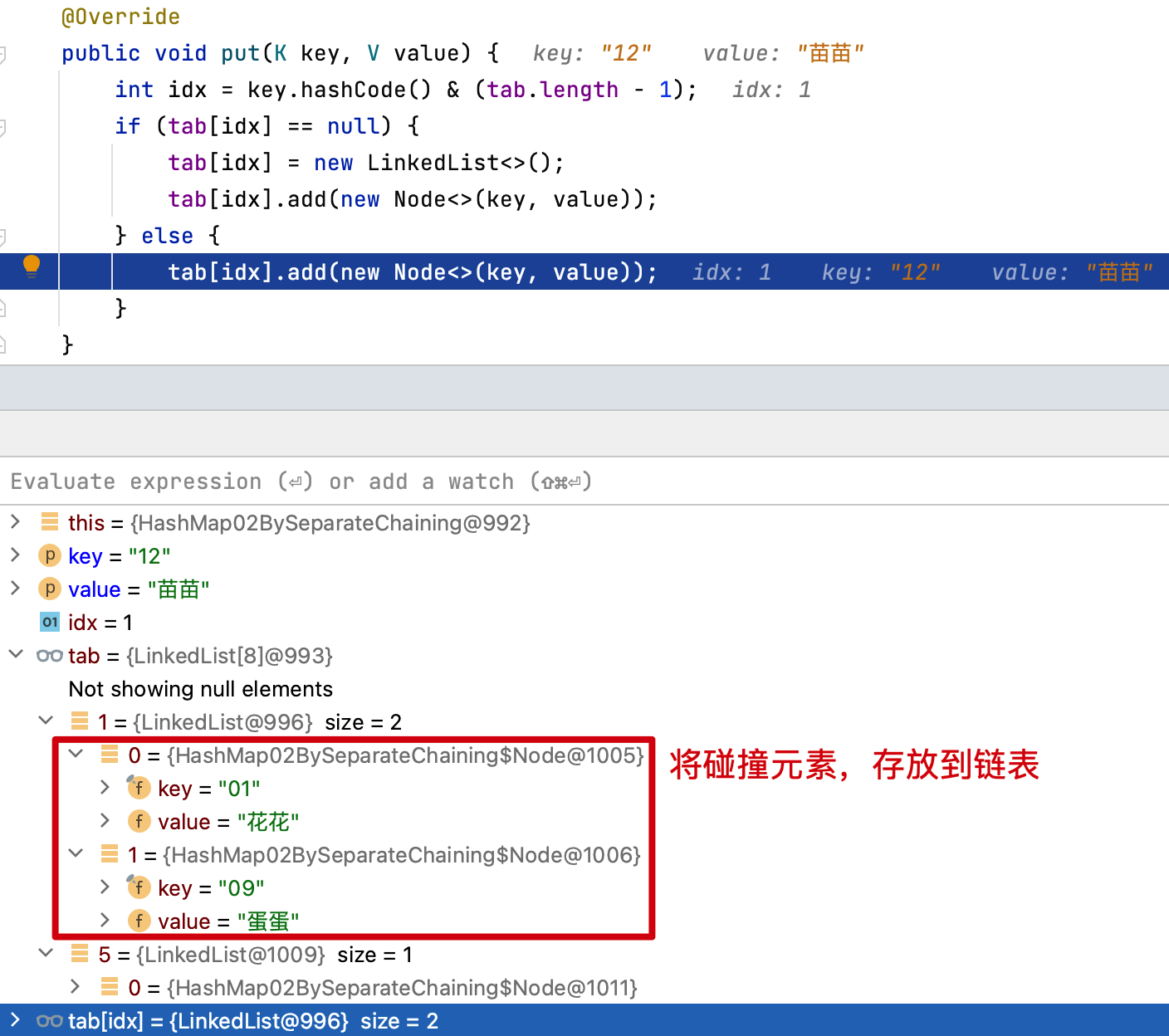
- 此时第一次和第二次获取01位置的元素就都是
花花了,元素没有被替代。因为此时的元素是被存放到链表上了。
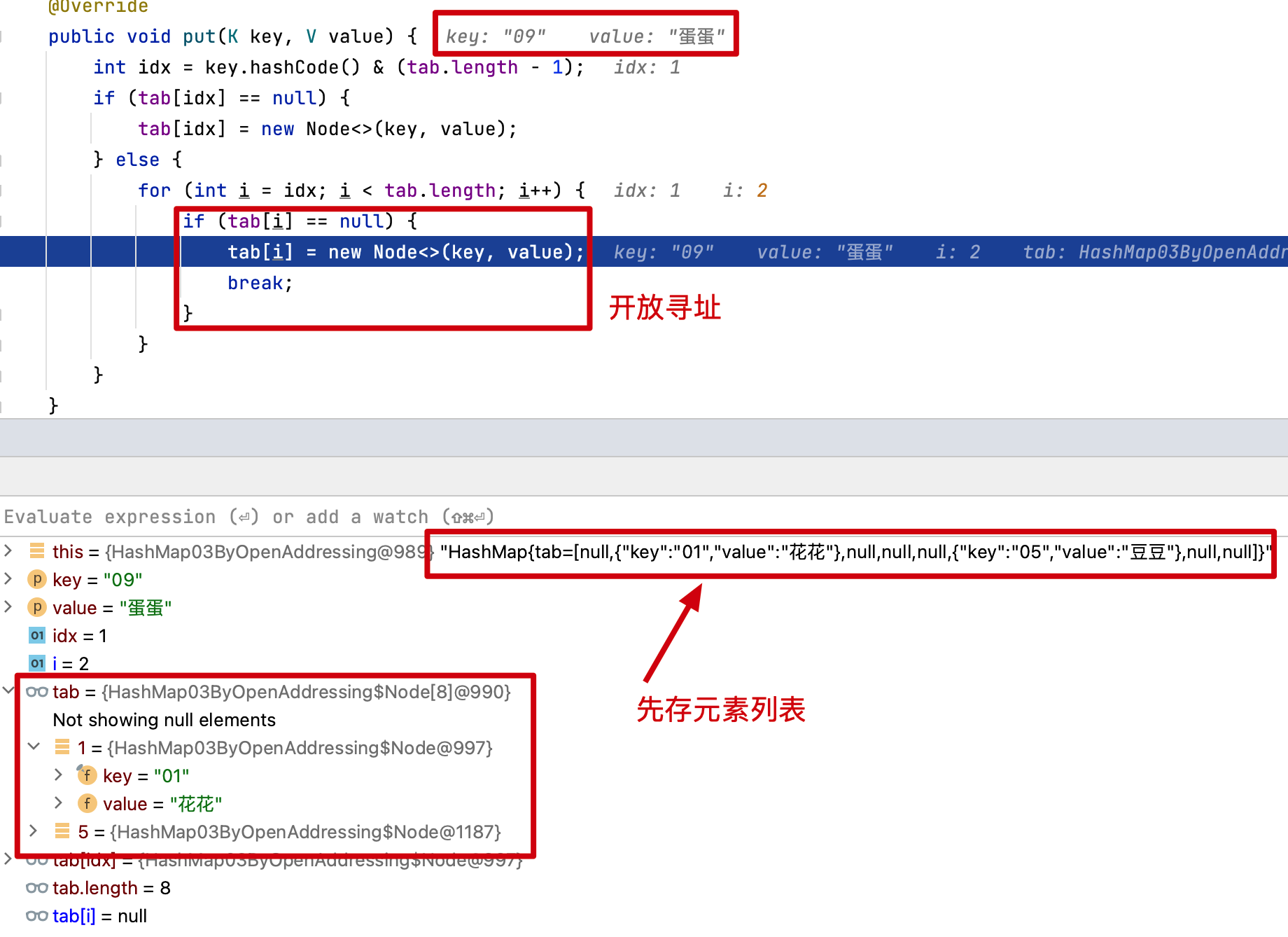
# 3. 开放寻址
说明:除了对哈希桶上碰撞的索引元素进行拉链存放,还有不引入新的额外的数据结构,只是在哈希桶上存放碰撞元素的方式。它叫开放寻址,也就是 ThreaLocal 中运用斐波那契散列+开放寻址的处理方式。
public class HashMap03ByOpenAddressing<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final Node<K, V>[] tab = new Node[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
if (tab[idx] == null) {
tab[idx] = new Node<>(key, value);
} else {
for (int i = idx; i < tab.length; i++) {
if (tab[i] == null) {
tab[i] = new Node<>(key, value);
break;
}
}
}
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
for (int i = idx; i < tab.length; i ++){
if (tab[idx] != null && tab[idx].key == key) {
return tab[idx].value;
}
}
return null;
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
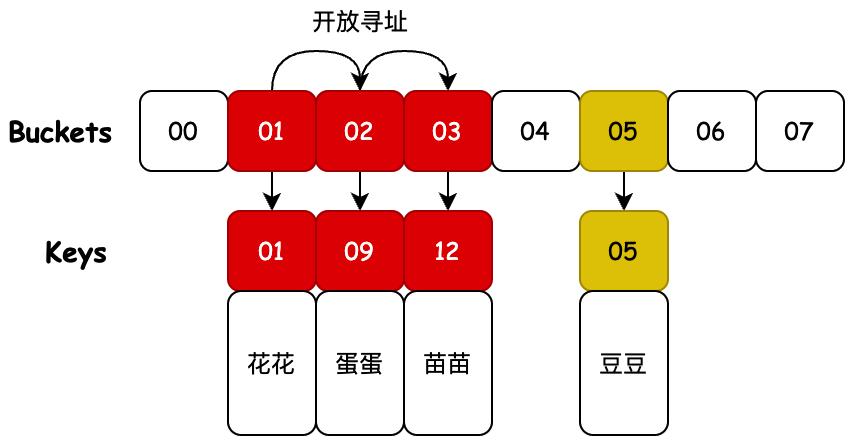
- 开放寻址的设计会对碰撞的元素,寻找哈希桶上新的位置,这个位置从当前碰撞位置开始向后寻找,直到找到空的位置存放。
- 在 ThreadLocal 的实现中会使用斐波那契散列、索引计算累加、启发式清理、探测式清理等操作,以保证尽可能少的碰撞。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap03() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap03ByOpenAddressing<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("05", "豆豆");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
07:20:22.382 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:20:22.387 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:20:22.387 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:HashMap{tab=[null,{"key":"01","value":"花花"},{"key":"09","value":"蛋蛋"},{"key":"12","value":"苗苗"},null,{"key":"05","value":"豆豆"},null,null]}
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
- 通过测试结果可以看到,开放寻址对碰撞元素的寻址存放,也是可用解决哈希索引冲突问题的。
# 4. 合并散列
说明:合并散列是开放寻址和单独链接的混合,碰撞的节点在哈希表中链接。此算法适合固定分配内存的哈希桶,通过存放元素时识别哈希桶上的最大空槽位来解决合并哈希中的冲突。
public class HashMap04ByCoalescedHashing<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final Node<K, V>[] tab = new Node[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
if (tab[idx] == null) {
tab[idx] = new Node<>(key, value);
return;
}
int cursor = tab.length - 1;
while (tab[cursor] != null && tab[cursor].key != key) {
--cursor;
}
tab[cursor] = new Node<>(key, value);
// 将碰撞节点指向这个新节点
while (tab[idx].idxOfNext != 0){
idx = tab[idx].idxOfNext;
}
tab[idx].idxOfNext = cursor;
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
while (tab[idx].key != key) {
idx = tab[idx].idxOfNext;
}
return tab[idx].value;
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
int idxOfNext;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
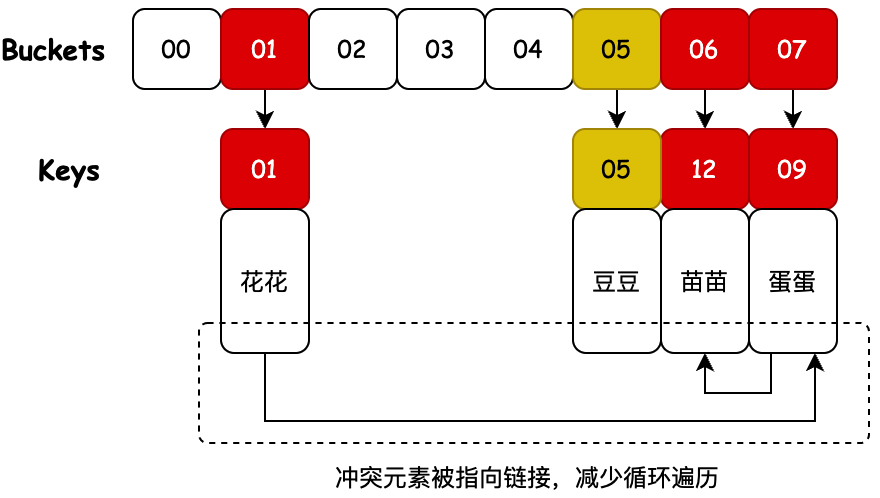
- 合并散列的最大目的在于将碰撞元素链接起来,避免因为需要寻找碰撞元素所发生的循环遍历。也就是A、B元素存放时发生碰撞,那么在找到A元素的时候可以很快的索引到B元素所在的位置。
测试
07:18:43.613 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:18:43.618 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:苗苗
07:18:43.619 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:HashMap{tab=[null,{"idxOfNext":7,"key":"01","value":"花花"},null,null,null,{"idxOfNext":0,"key":"05","value":"豆豆"},{"idxOfNext":0,"key":"12","value":"苗苗"},{"idxOfNext":6,"key":"09","value":"蛋蛋"}]}
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
- 相对于直接使用开放寻址,这样的挂在链路指向的方式,可以提升索引的性能。因为在实际的数据存储上,元素的下一个位置不一定空元素,可能已经被其他元素占据,这样就增加了索引的次数。所以使用直接指向地址的方式,会更好的提高索引性能。
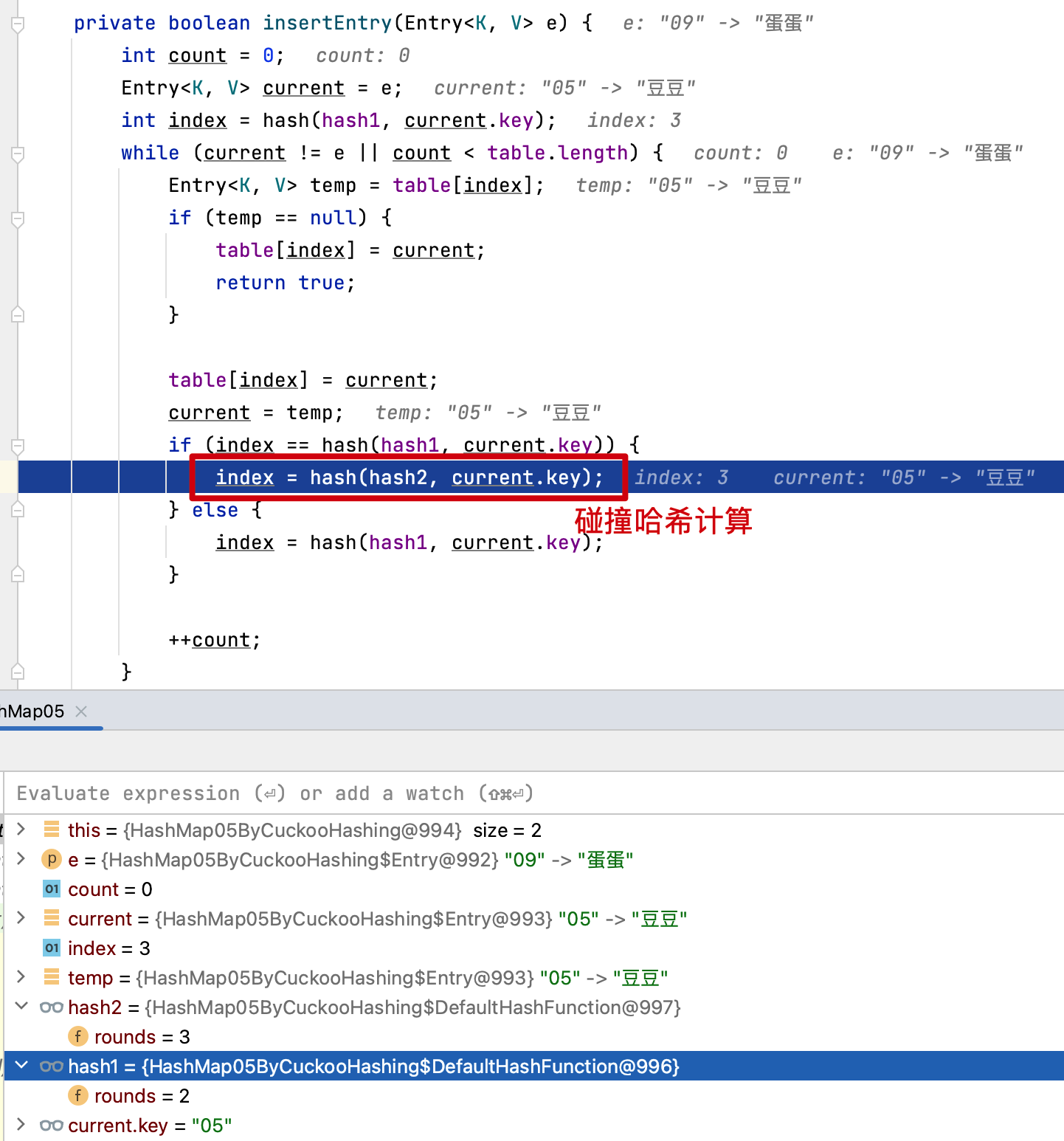
# 5. 杜鹃散列
说明:这个名字起的比较有意思,也代表着它的数据结构。杜鹃鸟在孵化🐣的时候,雏鸟会将其他蛋或幼崽推出巢穴;类似的这个数据结构会使用2组key哈希表,将冲突元素推到另外一个key哈希表中。
private V put(K key, V value, boolean isRehash) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
if (containsKey(k)) {
return null;
}
if (insertEntry(new Entry<K, V>((K) k, value))) {
if (!isRehash) {
size++;
}
return null;
}
rehash(2 * table.length);
return put((K) k, value);
}
private boolean insertEntry(Entry<K, V> e) {
int count = 0;
Entry<K, V> current = e;
int index = hash(hash1, current.key);
while (current != e || count < table.length) {
Entry<K, V> temp = table[index];
if (temp == null) {
table[index] = current;
return true;
}
table[index] = current;
current = temp;
if (index == hash(hash1, current.key)) {
index = hash(hash2, current.key);
} else {
index = hash(hash1, current.key);
}
++count;
}
return false;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
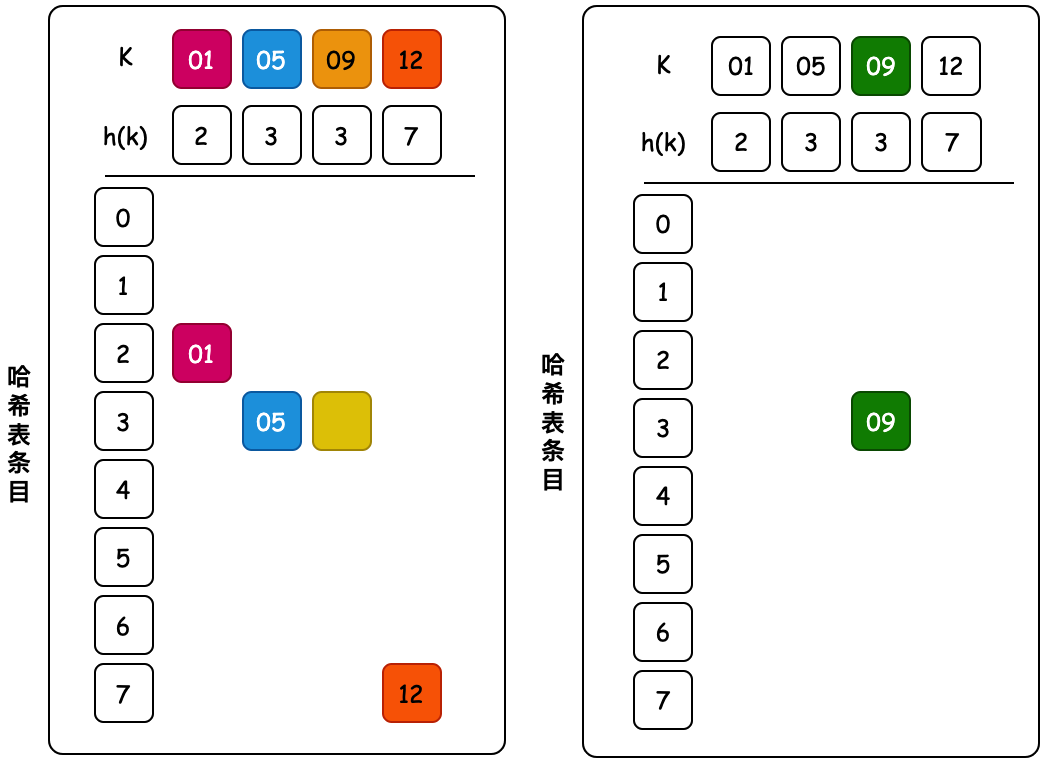
- 当多个键映射到同一个单元格时会发生这种情况。杜鹃散列的基本思想是通过使用两个散列函数而不是仅一个散列函数来解决冲突。
- 这为每个键在哈希表中提供了两个可能的位置。在该算法的一种常用变体中,哈希表被分成两个大小相等的较小的表,每个哈希函数都为这两个表之一提供索引。两个散列函数也可以为单个表提供索引。
- 在实践中,杜鹃哈希比线性探测慢约 20-30%,线性探测是常用方法中最快的。然而,由于它对搜索时间的最坏情况保证,当需要实时响应率时,杜鹃散列仍然很有价值。杜鹃散列的一个优点是它的无链接列表属性,非常适合 GPU 处理。
测试
07:52:04.010 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:52:04.016 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:苗苗
07:52:04.016 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:{01=花花, 12=苗苗, 05=豆豆, 09=蛋蛋}
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
- 从测试结果可以看到,杜鹃散列可以通过两个散列函数解决索引冲突问题。不过这个探测的过程比较耗时。
# 6. 跳房子散列
说明:跳房子散列是一种基于开放寻址的算法,它结合了杜鹃散列、线性探测和链接的元素,通过桶邻域的概念——任何给定占用桶周围的后续桶,也称为“虚拟”桶。 该算法旨在在哈希表的负载因子增长超过 90% 时提供更好的性能;它还在并发设置中提供了高吞吐量,因此非常适合实现可调整大小的并发哈希表。
public boolean insert(AnyType x) {
if (!isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
int currentPos = findPos(x);
if (currentPos == -1) {
return false;
}
if (array[currentPos] != null) {
x = array[currentPos].element;
array[currentPos].isActive = true;
}
String hope;
if (array[currentPos] != null) {
hope = array[currentPos].hope;
x = array[currentPos].element;
} else {
hope = "10000000";
}
array[currentPos] = new HashEntry<>(x, hope, true);
theSize++;
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
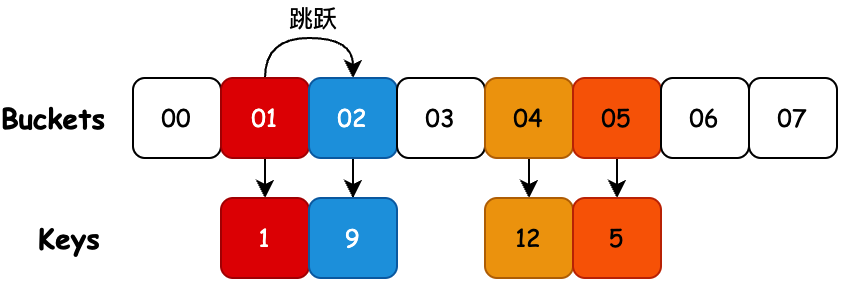
- 该算法使用一个包含n 个桶的数组。对于每个桶,它的邻域是H个连续桶的小集合(即索引接近原始散列桶的那些)。邻域的期望属性是在邻域的桶中找到一个项目的成本接近于在桶本身中找到它的成本(例如,通过使邻域中的桶落在同一缓存行中)。在最坏的情况下,邻域的大小必须足以容纳对数个项目(即它必须容纳 log( n ) 个项目),但平均只能是一个常数。如果某个桶的邻域被填满,则调整表的大小。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap06() {
HashMap06ByHopscotchHashing<Integer> map = new HashMap06ByHopscotchHashing<>();
map.insert(1);
map.insert(5);
map.insert(9);
map.insert(12);
logger.info("数据结构:{}", map);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
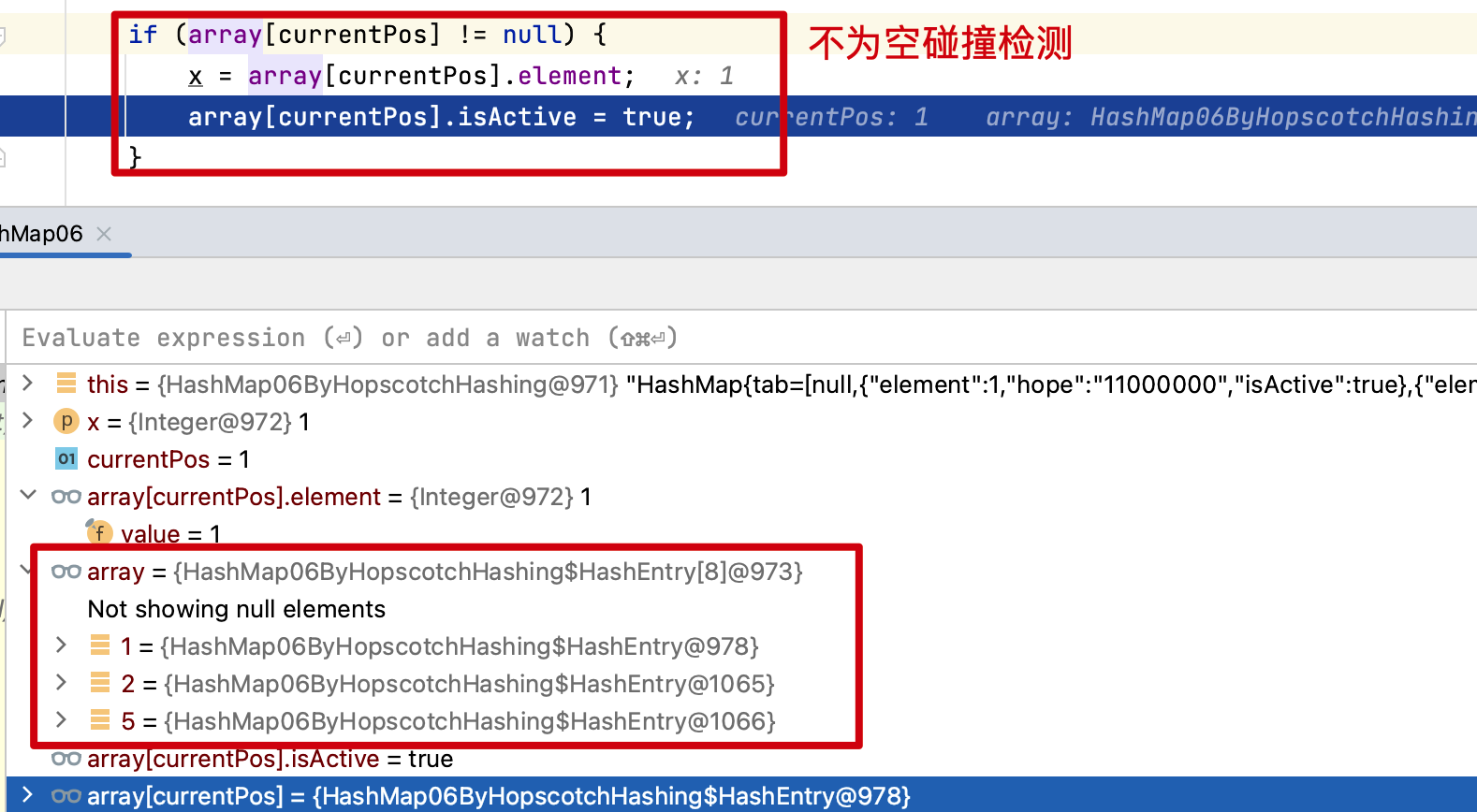
17:10:10.363 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:HashMap{tab=[null,{"element":1,"hope":"11000000","isActive":true},{"element":9,"hope":"00000000","isActive":true},null,{"element":12,"hope":"10000000","isActive":true},{"element":5,"hope":"10000000","isActive":true},null,null]}
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
- 通过测试可以看到,跳房子散列会在其原始散列数组条目中找到,或者在接下来的H-1个相邻条目之一找到对应的冲突元素。
# 7. 罗宾汉哈希
说明:罗宾汉哈希是一种基于开放寻址的冲突解决算法;冲突是通过偏向从其“原始位置”(即项目被散列到的存储桶)最远或最长探测序列长度(PSL)的元素的位移来解决的。
public void put(K key, V value) {
Entry entry = new Entry(key, value);
int idx = hash(key);
// 元素碰撞检测
while (table[idx] != null) {
if (entry.offset > table[idx].offset) {
// 当前偏移量不止一个,则查看条目交换位置,entry 是正在查看的条目,增加现在搜索的事物的偏移量和 idx
Entry garbage = table[idx];
table[idx] = entry;
entry = garbage;
idx = increment(idx);
entry.offset++;
} else if (entry.offset == table[idx].offset) {
// 当前偏移量与正在查看的检查键是否相同,如果是则它们交换值,如果不是,则增加 idx 和偏移量并继续
if (table[idx].key.equals(key)) {
// 发现相同值
V oldVal = table[idx].value;
table[idx].value = value;
} else {
idx = increment(idx);
entry.offset++;
}
} else {
// 当前偏移量小于我们正在查看的我们增加 idx 和偏移量并继续
idx = increment(idx);
entry.offset++;
}
}
// 已经到达了 null 所在的 idx,将新/移动的放在这里
table[idx] = entry;
size++;
// 超过负载因子扩容
if (size >= loadFactor * table.length) {
rehash(table.length * 2);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
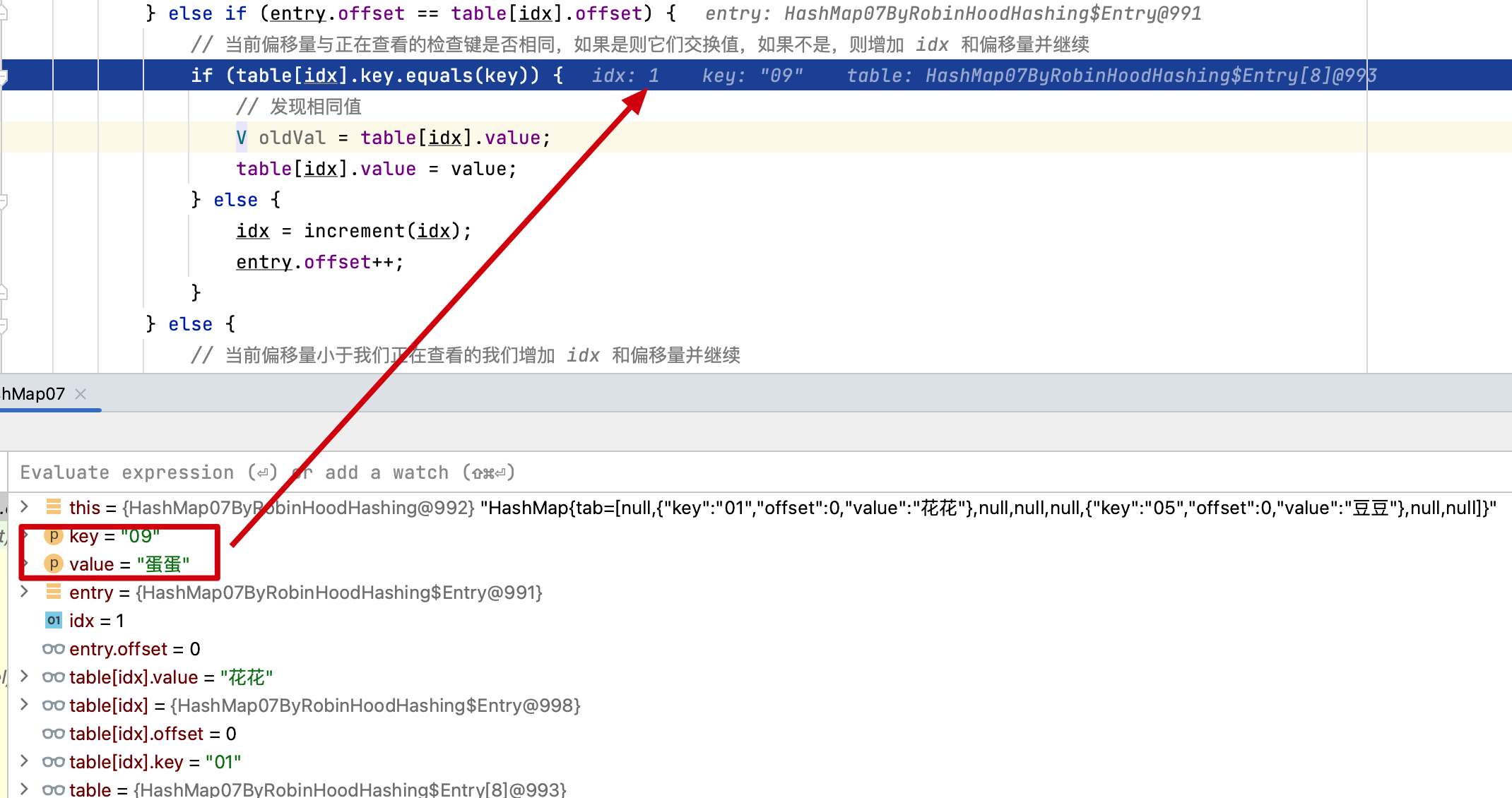
- 09、12 和 01 发生哈希索引碰撞,进行偏移量计算调整。通过最长位置探测碰撞元素位移来处理。
测试
public void test_hashMap07() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap07ByRobinHoodHashing<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("05", "豆豆");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("12"));
logger.info("数据结构:{}", map);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
07:34:32.593 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
09 1
12 1
01 1
09 9
12 1
05 5
07:35:07.419 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:苗苗
07:35:07.420 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:HashMap{tab=[null,{"key":"01","offset":0,"value":"花花"},{"key":"12","offset":1,"value":"苗苗"},null,null,{"key":"05","offset":0,"value":"豆豆"},null,null,null,{"key":"09","offset":0,"value":"蛋蛋"},null,null,null,null,null,null]}
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 通过测试结果和调试的时候可以看到,哈希索引冲突是通过偏向从其“原始位置”(即项目被散列到的存储桶)最远或最长探测序列长度(PSL)的元素的位移来解决。这块可以添加断点调试验证。
# 四、常见面试问题
- 介绍一下散列表
- 为什么使用散列表
- 拉链寻址和开放寻址的区别
- 还有其他什么方式可以解决散列哈希索引冲突
- 对应的Java源码中,对于哈希索引冲突提供了什么样的解决方案
